Two models seem convenient for new sellers when it comes to selling products online: Amazon FBA and dropshipping.
Both Amazon FBA and dropshipping can generate substantial profits, but they serve different entrepreneurial needs. The dropshipping success rate is only around 10–20% compared to the slightly higher Amazon FBA success rate of 11–25%, where 64% of Amazon sellers become profitable within 12 months.
Launching an online business has never been more accessible, yet choosing between Amazon FBA and dropshipping remains one of the most critical decisions new entrepreneurs face.
That’s why I’ve created this detailed Amazon FBA vs Dropshipping comparison to help you choose the right model for your online business.
What is Amazon FBA?
Amazon FBA transforms you into an inventory owner who leverages Amazon’s massive logistics network to reach customers worldwide.

Amazon FBA is a service that facilitates product warehousing and shipping processes for businesses. With Amazon FBA, eCommerce store owners can send their products to Amazon’s fulfillment center instead of setting up their own warehouse.
In this model, you purchase products upfront, store them in Amazon’s warehouses, and Amazon handles everything from customer orders to returns. Products listed as FBA qualify for Amazon Prime’s two-day (or even same-day) shipping, making them more appealing to the millions of Prime members worldwide.
How Amazon FBA Operations Work
The FBA process follows a straightforward path: research profitable products, source them from suppliers, ship inventory to Amazon fulfillment centers, and let Amazon handle customer orders.
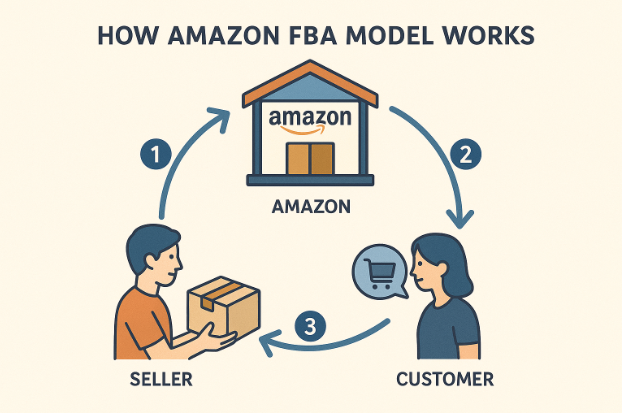
Amazon processes the customer’s payment, deducts FBA fees, and deposits the balance into your seller account.
Key FBA Requirements:
- Upfront inventory investment
- Product sourcing and quality control
- Amazon warehouse shipping
- Compliance with Amazon’s packaging standards
What is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping eliminates inventory ownership entirely, positioning you as a middleman between suppliers and customers.
Amazon dropshipping is a business model where you sell products on Amazon without storing them and delivering to the customers yourself. Instead of keeping inventory, you purchase the product from a third-party supplier after a customer places an order.
This model allows you to test multiple products without financial commitment. Because you don’t have to purchase inventory, you can try out new products and see how they perform. You can list an extensive range of products without having to carry stock.
How Dropshipping Operations Work
The dropshipping workflow is elegantly simple: list products from suppliers, receive customer orders, forward orders to suppliers, and suppliers ship directly to customers.
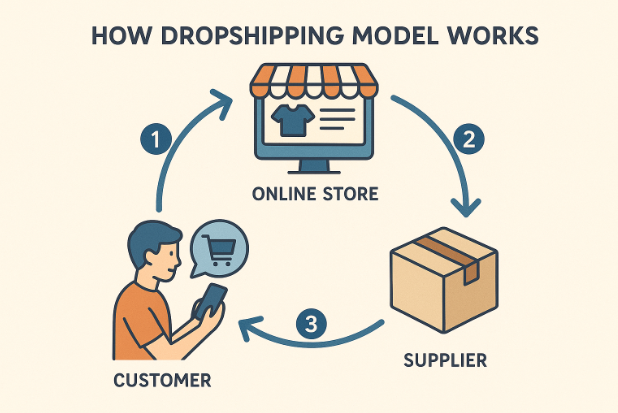
Amazon’s strict dropshipping policy requires that you, the seller, are listed as the “seller of record” on all shipments.
Financial Investment Comparison: Startup Costs
The capital requirements between these models differ dramatically and often determine which path entrepreneurs can realistically pursue.
Amazon FBA Investment Requirements
Amazon FBA demands significant upfront capital across multiple categories. Most new Amazon FBA sellers tend to spend between $2,500 and $5,000 to get started. This range covers essential expenses like inventory, marketing, and Amazon fees.
Detailed FBA Cost Breakdown:
- Inventory Investment: Typically ranging from $500 to $5,000 depending on product type and quantity
- Professional Seller Account: $39.99 monthly subscription
- Product Barcodes: $30 from GS1 for single UPC codes
- Marketing Budget: Amazon PPC: Pay-per-click campaigns can be a powerful tool to boost visibility. Budget at least $100 to $500 monthly
Amazon FBA startup costs are between $100 and $20,000+, though most sellers find success starting in the $1,000-$3,000 range.
Dropshipping Investment Requirements
Dropshipping’s appeal lies in its minimal financial barriers. You don’t need to spend thousands of dollars to buy inventory upfront, so there’s minimal financial risk.
Typical Dropshipping Startup Costs:
- Website Setup: $200-$500 for basic e-commerce platform
- Product Samples: Approximately $50 to verify product quality before bulk ordering
- Marketing Investment: Basic advertising on Facebook can cost anywhere from $5-$50 per day
- Business Registration: Optional but recommended
Starting a dropshipping business can be done with as little as $200 to $500. This budget covers the cost of setting up a website, initial marketing, and any necessary business expenses.
Profit Margins and Earning Potential
Understanding the financial returns of each model helps set realistic expectations and inform strategic decisions.
Amazon FBA Profitability
FBA typically offers higher profit margins per sale due to reduced competition and premium positioning. You’ll pay referral fees, FBA pick-and-pack fees, and storage fees. On average, you can expect around 15-30% of each sale to go toward Amazon’s costs.
However, successful FBA sellers often achieve substantial monthly revenues. Most Amazon sellers can expect to bring home no more than $5,000/month in profit, though top performers earn significantly more.
Dropshipping Profitability
Dropshipping operates on thinner margins but requires less capital investment. The average margin for dropshipping stores ranges from 10% to 30%, but your average will differ based on your business model, niche, and products.
On average, profit margins range from 15% to 20%, depending on the niche and product price. While individual sale profits are smaller, the model’s scalability can generate substantial cumulative returns.
Advantages of Amazon FBA
Amazon FBA offers several compelling benefits that attract serious entrepreneurs looking to build substantial businesses.
1. Prime Badge and Customer Trust
Your products are automatically eligible for Prime Two-Day Shipping which will boost shopper confidence. This Prime eligibility significantly increases conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
2. Operational Simplicity
Amazon handles the complex logistics that typically burden e-commerce businesses. Amazon takes care of picking, packing, shipping, refunds, and returns, allowing you to focus on product development and marketing strategy.
3. Scalability and Growth Potential
During the 2019 U.S. holiday season, independent third-party sellers—mostly small and medium-sized businesses—sold and shipped over 100 million items with Prime Free One-Day Delivery, demonstrating the platform’s massive scale potential.
4. Professional Infrastructure
Amazon handles customer service and returns, providing a high standard of support that boosts customer satisfaction and encourages repeat purchases.
Disadvantages of Amazon FBA
Despite its advantages, FBA presents significant challenges that can impact profitability and operational flexibility.
1. High Upfront Investment
FBA requires an upfront investment in inventory, which can be a financial burden, especially if products don’t sell as per expectations. This creates substantial financial risk for new entrepreneurs.
2. Complex Fee Structure
Amazon’s fee system can quickly erode profit margins. Amazon charges various fees, including fulfillment fees (based on item size and weight), referral fees (a percentage of the sale price), and long-term storage fees for items that remain in Amazon’s warehouses beyond a set period.
3. Limited Brand Control
Amazon’s strict seller policies also limit control over branding and impose guidelines that sellers must adhere to, adding another layer of compliance.
Advantages of Dropshipping
Dropshipping appeals to entrepreneurs seeking flexibility and minimal risk exposure.
1. Minimal Startup Risk
You don’t need to spend money on inventory or a business premises to get started with dropshipping. The only costs involved are setting up an online store, ordering a few samples to find the right supplier and marketing costs.
2. Product Testing Flexibility
If a product doesn’t sell, you can quickly drop it and try a different product. With traditional e-commerce and Amazon FBA, you would have to invest in expanding your inventory to extend your range of products.
3. Location Independence
Dropshipping also allows you to run a business from any place where there is an internet connection, providing unprecedented operational freedom.
4. Passive Income Potential
When your dropshipping store is set up and generating sales, you can make money while you sleep, though this requires initial effort to establish systems and traffic.
Disadvantages of Dropshipping
Dropshipping’s accessibility comes with trade-offs that can limit long-term success potential.
1. Thin Profit Margins
Although the startup costs are low, dropshipping often operates on thin profit margins. This makes scaling more challenging and requires higher sales volumes to achieve substantial income.
2. Quality Control Challenges
Since the products you’re selling will be shipped directly from the manufacturer or supplier, there is no way for you to control the quality of the product.
3. Shipping Complications
Managing shipping times and costs can be tricky, especially if you’re working with multiple suppliers who have different shipping policies. This can lead to longer delivery times and higher shipping costs for customers.
4. High Competition
Since it is much easier to start dropshipping, there is also much more competition, making it harder to establish market differentiation.
When to Choose Amazon FBA
FBA suits entrepreneurs with specific characteristics and business objectives.
Choose FBA When:
- You have $2,000+ in startup capital
- You want to build a scalable, sellable business asset
- Prime eligibility is crucial for your target market
- You prefer fewer competitors in your product space
- You can handle inventory management and forecasting
If you’re working with a product priced between $15 and $85 and carrying solid profit margins, these fees are much less of a concern.
When to Choose Dropshipping
Dropshipping works best for specific entrepreneurial situations and goals.
Choose Dropshipping When:
- You have limited startup capital (under $1,000)
- You want to test multiple product ideas quickly
- You prefer location independence and flexibility
- You’re comfortable with lower profit margins per sale
- You want to start immediately without inventory investment
Yes, dropshipping is a great option for beginners due to its low startup costs and minimal risk. It allows newcomers to start an online business without needing significant capital.
Also Read:
Conclusion: Dropshipping is Best For Beginners; Professional Sellers Can Choose Amazon FBA
The choice between Amazon FBA and dropshipping ultimately comes down to your financial situation, risk tolerance, and business aspirations. Both models have proven their viability in 2025, but they cater to different entrepreneurial profiles and goals.
Amazon FBA is ideal for entrepreneurs who have substantial startup capital and want to build a serious, scalable business. The higher upfront investment translates to better profit margins, Prime eligibility, and a more professional customer experience. However, this model requires significant financial commitment and carries higher inventory risk.
Dropshipping, on the other hand, democratizes entrepreneurship by removing financial barriers to entry. It’s perfect for beginners who want to test the e-commerce waters without major financial risk. The trade-off is thinner profit margins, increased competition, and less control over the customer experience.